The evolution of online consumer behavior : what’s changed and what hasn’t
You have seen online buying shift from desktop catalogs to mobile-first shopping, driven by social cues, fast delivery and data-powered personalization; you now expect seamless experiences yet face data privacy risks and misinformation that can harm trust, while persistent behaviors like price sensitivity and desire for reviews remain unchanged. Understanding these trends helps you adapt marketing, product and service strategies to protect customer trust and leverage personalization and convenience.
Key Takeaways:
- Mobile-first shopping now dominates visits and conversions, forcing designs and checkouts optimized for small screens and app experiences.
- Personalization and AI-driven recommendations increasingly influence purchase decisions, while consumers expect relevant, timely content.
- Privacy and trust remain top concerns; consent-driven, cookieless strategies and transparent data practices reshape marketing and analytics.
- Omnichannel convenience and faster fulfillment-same-day delivery, BOPIS, easy returns-are standard expectations, not differentiators.
- Persistent behaviors include price sensitivity, reliance on reviews and social proof, and preference for clear value and reliable service.
The Historical Context of Online Consumer Behavior
Early Days of E-Commerce
When you first encountered online stores in the mid‑1990s, the landscape was dominated by pioneers like Amazon (founded 1994) and eBay (founded 1995), and transactions were constrained by dial‑up speeds (often 28.8-56 kbps) and early encryption standards-Netscape’s SSL rolled out in the mid‑90s to bolster trust. Your buying decisions then were shaped by limited catalogs, slow pages, and the need to trust that entering a credit card online wouldn’t lead to fraud; merchants countered with simple trust signals like visible contact details, 800 numbers and explicit return promises.
Traffic and conversion metrics were tiny by today’s standards: U.S. e‑commerce sales were only in the low tens of billions by 2000 (roughly $27 billion), so companies experimented aggressively with payment and trust mechanisms-PayPal and similar services emerged in the late‑90s to reduce friction, while the dot‑com bust forced many retailers to refine unit economics and focus on sustainable customer acquisition rather than pure growth at any cost. You benefited from early price arbitrage but paid the price of unpredictable delivery times and limited customer service.
The Rise of Internet Accessibility
Broadband adoption through the 2000s and the launch of the iPhone in 2007 fundamentally changed how you access stores: pages loaded faster, images and video became standard, and apps created persistent brand presence on your device. Global internet penetration climbed from under 1% in 1995 to over 60% by 2020, and by the mid‑2010s mobile traffic began to surpass desktop for many categories-shifting the performance and design priorities for every retailer you interact with.
As connectivity improved, your expectations shifted toward immediacy and convenience: micro‑moments-search, compare, buy on the go-became everyday behavior, and smartphone ownership in developed markets climbed above 80% by the late 2010s, enabling a steady rise in app‑based commerce and push‑driven marketing. Retailers had to redesign funnels for thumb navigation, one‑click flows and simplified checkout to capture those impulsive, high‑intent interactions.
Network upgrades (3G → 4G → LTE, and later 5G in pockets) plus cheaper smartphones and data plans let many emerging markets leapfrog desktop: you began making entire purchase journeys on a single device, with mobile wallets and one‑touch payments cutting abandonment and expanding market reach for retailers that optimized for small screens and intermittent connectivity.
The Transition from Brick-and-Mortar to Digital
Major retail chains shifted strategy as you started buying more online: Amazon scaled Prime (launched 2005) to lock in repeat purchases, while incumbents like Walmart and Target invested heavily in e‑commerce and last‑mile pickup. By 2019 U.S. e‑commerce represented roughly 11% of total retail sales, and the proliferation of digitally native brands (Warby Parker, Glossier, Casper) taught you to expect direct‑to‑consumer convenience and tight brand storytelling.
Operational innovations shaped your experience: free shipping, easy returns, and services like BOPIS (buy‑online‑pickup‑in‑store) became standard competitive levers. The pandemic then accelerated adoption-online share jumped further as consumers moved non‑discretionary and grocery spending online-forcing retailers to scale fulfillment, adapt pricing strategies and rethink in‑store roles as fulfillment hubs.
Behind the scenes, you’ve seen retailers overhaul logistics and merchandising: investments in inventory pooling, micro‑fulfillment centers, and real‑time personalization powered by data science reduced lead times but raised last‑mile costs; at the same time, advanced recommendation engines increased average order values and cemented personalization as a baseline expectation rather than a luxury.
Factors Influencing Online Consumer Behavior
- Technological Advances
- Socioeconomic Dynamics
- Psychological Factors
- After device and demographic differences are accounted for, channel mix and trust still explain most conversion variance.
Technological Advances
You see the impact of faster networks and smarter interfaces every time a page loads in under two seconds: page speed still drives conversion, with studies showing mobile abandonment spikes when load time exceeds three seconds. Adoption of 5G, progressive web apps (PWAs) and app-centric experiences has raised baseline expectations-brands that use AI personalization and recommendation engines (Amazon attributes roughly 35% of sales to recommendations) deliver notably higher basket sizes and repeat purchases.
Platforms that integrate immersive tech also change purchase behavior; try-on AR tools from beauty and furniture retailers reduce returns and increase confidence, and live commerce formats (notably in China) have demonstrated conversion rates multiple times higher than standard listings. Meanwhile, privacy shifts-GDPR, CCPA and the deprecation of third-party cookies-force you to pivot to first-party data strategies and server-side measurement to preserve targeting and attribution.
Socioeconomic Dynamics
Rising internet access and expanding middle classes in Southeast Asia, Africa and Latin America mean more first-time online shoppers, and you must adapt pricing, payment and logistics accordingly: mobile wallets, cash-on-delivery and local payment rails like M-Pesa remain decisive in many markets, while reliable last-mile delivery is a major purchase trigger.
Behavior also diverges by age and life stage-Gen Z and younger Millennials favor social commerce, short-form video and seamless in-app purchases, whereas older cohorts often prioritize clear returns and phone support. Platforms such as TikTok and Instagram have accelerated discovery-driven buying, with social proof and creator endorsements converting at rates brands struggle to match on traditional channels.
More granularly, economic volatility increases price sensitivity: during inflationary periods you’ll see higher cart abandonment and greater uptake of BNPL (buy-now-pay-later) and subscription discounts. Loyalty programs that offer immediate, tangible savings (e.g., free shipping thresholds, instant discounts) outperform point-only schemes in sustaining repeat behavior.
Psychological Factors
Trust and social proof remain powerful: you are far more likely to buy when ratings, verified reviews and clear return policies reduce perceived risk-listings with strong reviews and transparent policies commonly show double-digit lifts in conversion. Cognitive shortcuts such as defaults, scarcity cues and urgency timers also alter the decision path; A/B tests frequently demonstrate measurable lifts from well-timed nudges, but those gains can erode long-term trust if overused.
Emotional drivers-status, identity, fear of missing out-interact with heuristics: you respond to curated bundles, anchoring price points, and hard-to-compare choices by choosing the simplest, most familiar option. Behavioral economics tactics work best when combined with rigorous measurement and ethical guardrails to avoid manipulative dark patterns.
- Trust & Reviews
- Scarcity & Urgency
- Any behavioral nudge must be tested for lift and reviewed for its long-term effect on loyalty.
Delving deeper, personalization that accounts for your prior engagement, basket history and channel preference reduces friction and increases lifetime value, but it also raises expectations about privacy and transparency-explicit consent, clear value exchange and options to control personalization are necessary to maintain trust while leveraging behavioral levers. Any overreach (e.g., using overly aggressive scarcity when inventory is ample) risks backfiring and harming your brand reputation.
The Role of Social Media in Consumer Engagement
Platforms Shaping Consumer Preferences
Major platforms have become the primary discovery channels you rely on: Instagram (now over 2 billion monthly active users), TikTok (surpassed 1 billion MAUs), and Facebook (around 3 billion) each push different purchase triggers through formats like Reels, short-form video, and integrated Shops. For example, e.l.f.’s TikTok campaign “Eyes.Lips.Face” generated billions of views and measurable uplifts in sales, while Gymshark scaled to a near-$1 billion valuation largely by leveraging influencer-driven Instagram content to build community-led demand.
Audience composition matters: Pew Research shows TikTok skews heavily toward younger adults (nearly half of 18-29-year-olds use it), so you’ll find trend-driven impulse purchases there, whereas Facebook and YouTube remain more effective for research-oriented shoppers. Live commerce-already a multibillion-dollar channel in China-illustrates how platform features (live Q&A, instant checkout) convert attention into immediate transactions, meaning your choice of platform directly shapes how and when customers buy.
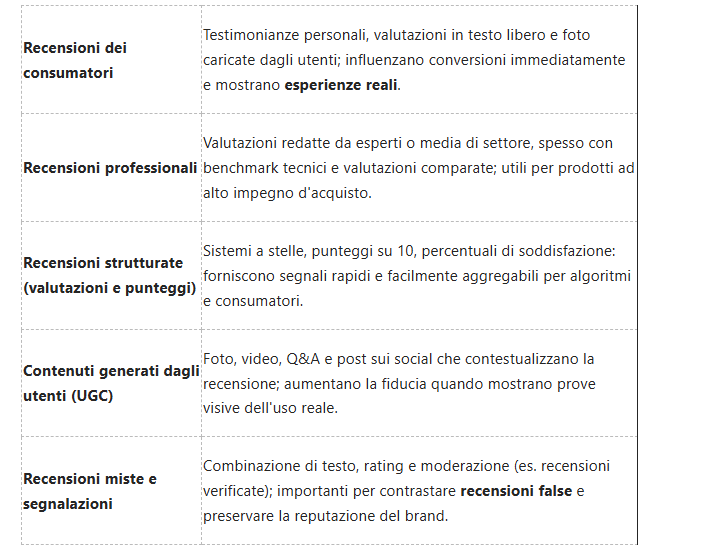
The Influence of User-Generated Content
User-generated content (UGC) now carries exceptional persuasive power: studies report that roughly 79% of consumers say UGC highly impacts their purchase decisions, so you should prioritize real customer photos, unboxing videos, and peer reviews on product pages and ads. Brands like GoPro and Patagonia amplify organic creator content to demonstrate real-world use cases, and you’ll see higher engagement when customers recognize peers rather than polished ads.
From a performance standpoint, featuring UGC can raise your engagement and conversion metrics-merchants routinely report double-digit lifts in time-on-page and click-throughs when authentic customer content replaces or complements branded creative. Because UGC is cost-effective and scalable, you can use it to sustain long-term social proof without continuously funding high-cost production.
Be vigilant about moderation and authenticity: fake or incentivized posts can quickly erode trust and invite platform penalties. Platforms and marketplaces increasingly remove suspicious reviews and require verification; you should implement monitoring, verification badges, and clear submission rules to protect your brand’s credibility.
Social Proof and its Impact on Purchasing Decisions
Social proof-star ratings, review counts, influencer endorsements, “most popular” badges-shortens the path from consideration to purchase by reducing perceived risk; according to BrightLocal data, about 79% of consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations. You’ll notice that products with higher average ratings and substantial review volume consistently outperform comparable SKUs in conversion and placement on marketplaces.
Urgency and popularity cues amplify social proof: messages like “100 people are viewing this” or low-stock warnings create FOMO that can lift conversions by notable margins, often in the high-single to low-double digits depending on the category. Testing which combination of ratings, counts, and scarcity signals works for your audience will directly affect average order value and purchase velocity.
Watch for manipulation: fake reviews, undisclosed paid endorsements, and bots can inflate short-term metrics but damage long-term trust and violate regulations. The FTC requires disclosure of sponsored content and influencers’ compensation; you must enforce transparent endorsement practices and remove inauthentic reviews to safeguard both compliance and customer confidence.
Mobile Commerce and its Impact
Growth of Mobile Shopping
Your smartphone is now the default storefront: by 2023 mobile channels accounted for roughly about 70% of global e‑commerce traffic and a majority of transactions, with markets like China and India pushing that share even higher. Companies such as Alibaba and Shein built growth strategies around app-first experiences, and marketplaces optimized product discovery, reviews and checkout flows for one-handed use, which has driven both frequency and basket size on mobile.
Because you shop in short bursts throughout the day, merchants design experiences for micro‑moments-quick search, rapid checkout, and contextual offers-so impulse purchases and in‑store-to-online conversions rise. At the same time, increased mobile usage raises privacy and fraud exposure, forcing retailers to balance seamlessness with stronger authentication and fraud‑prevention tools.
Mobile App versus Mobile Web
When you use a dedicated app, you commonly see higher conversion rates: apps can convert at around 2-4× the rate of mobile web due to persistent login, saved payment methods and push notifications that drive repeat visits. Brands like Amazon and Starbucks leverage app features-personalized feeds, loyalty integration and offline caching-to lift average order value and customer lifetime value.
On the other hand, mobile web remains critical for acquisition and discovery because search, social links and shared URLs funnel users directly without app‑store friction; Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) bridge gaps-AliExpress’s PWA, for example, reported a significant lift in conversions for new users after deployment. You should weigh reach versus retention: web brings scale, apps bring deeper engagement.
More specifically, your decision to invest in an app should consider development and maintenance costs, app‑store approval delays, and the incremental revenue per retained user-most retailers see higher AOV and retention in apps (often 10-30% higher), but acquisition cost can be steeper, making a hybrid strategy (PWA + native app) attractive for many brands.
Mobile Wallets and Payment Systems
Integrating mobile wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, Alipay and WeChat Pay removes friction at checkout and can lift conversion by double‑digit percentages, especially on one‑tap flows or when combined with saved addresses and biometrics. In China, for instance, mobile wallets dominate digital payments-penetration often exceeds 80%-and international merchants that add local wallets see measurable uplifts in sales.
Beyond convenience, mobile wallets bring technical benefits: tokenization reduces card‑data exposure, biometrics lower chargeback risk, and SDKs can reduce your PCI footprint. Still, attacks on mobile payment flows and account takeovers remain a material risk, so you must implement device binding, risk scoring and fraud monitoring alongside the payment options you offer.
More practically, you’ll face tradeoffs-integrating regional wallets increases complexity and fees but unlocks market access; BNPL providers like Klarna or Afterpay boost average order value by letting you offer flexible payment options; and cross‑border merchants often see a 10-25% conversion lift after adding locally preferred wallets and payment rails.
The Importance of User Experience (UX)
Website Design and Navigation
Your layout should guide action: clear visual hierarchy, prominent calls-to-action, and predictable navigation reduce friction and increase conversion. Studies from the Nielsen Norman Group show users form impressions in under a second and often scan pages in an F-pattern, so placing primary actions and product details where the eye naturally lands is not optional-it's functional design. Implementing thumb-friendly controls and a simplified top-level menu for mobile can lift engagement noticeably; retailers that adopt a single-column mobile flow frequently report double-digit increases in mobile checkout completion.
Navigation patterns that hide options behind unclear icons or deep menus increase abandonment: Baymard Institute data links poor checkout flow to the web’s average cart abandonment rate of about 69.5%. You can reduce that by using persistent cart icons, breadcrumb trails, and contextual microcopy that tells users where they are and what comes next. When you remove ambiguity, you shorten decision time and lower drop-off across category pages and search results.
Personalization and Customer Journey
When you tailor content to behavior, the lift is measurable: recommendation engines account for roughly 35% of Amazon’s revenue, and broad industry work shows personalized experiences drive higher conversion and retention. Dynamic product lists, recently viewed carousels, and context-aware promotions move users from discovery to purchase faster because they match intent-if your signals are accurate. Segmenting by past purchases, referral source, or on-site behavior enables triggers like cart rescue emails and in-session promos that improve lifetime value.
At the same time, personalization introduces trade-offs you must manage. Data-driven suggestions increase relevance but can erode trust when you overreach or expose too much personal data; regulatory frameworks like GDPR and CCPA make consent flows and data minimization operational requirements. You should adopt transparent preference centers and let users control personalization levels to protect trust while maintaining performance.
To operationalize personalization, map the customer journey end-to-end and instrument each touchpoint with analytics and a customer data platform (CDP). Use A/B tests to validate whether your personalized pathways improve metrics such as conversion rate, average order value, and retention; prioritize experiments where the potential upside is largest-for instance, testing personalized checkout nudges for high-value cohorts or cross-sell bundles for repeat buyers.
Loading Time and its Implications
Page speed directly affects revenue and SEO: Google reported that mobile visitors are likely to abandon a page that takes more than 3 seconds to load, and Amazon’s internal analysis famously found that every 100ms of added latency cost about 1% in sales. You should treat load time as a conversion lever-optimizations such as image compression, critical CSS inlining, and a global CDN reduce friction immediately and improve both engagement and organic ranking via Core Web Vitals.
Technical fixes are only one side of the equation; prioritization matters. Focus first on metrics with the biggest user impact-Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), input responsiveness, and visual stability-then move to secondary improvements like caching policies and third-party script governance. Retailers that deferred nonvital scripts until after interactive paint often see bounce rates drop and checkout throughput rise within weeks.
Measure continuously with tools like Lighthouse, WebPageTest, and Google Analytics, and keep specific targets: aim for LCP under 2.5s, First Input Delay (or INP) below 100ms, and CLS under 0.1. Those thresholds not only improve user perception but also align your site with search ranking signals, turning performance investment into sustained traffic and conversion gains.
Changing Patterns in Consumer Trust
The Evolution of E-Commerce Trust Signals
You now judge a store in seconds by visible cues: an HTTPS padlock, clear return policies, and payment options that offer buyer protection. By 2023 over 95% of top sites used HTTPS, making the padlock a baseline rather than a differentiator; what actually moves the needle are dynamic trust signals like real-time inventory, visible delivery windows, and live chat that resolves pre-purchase questions. Google’s research still shows that slow load times destroy confidence-more than 50% of mobile visitors abandon pages that take over three seconds-so performance itself is a trust metric.
Examples matter: Amazon’s A-to-z Guarantee and PayPal’s buyer protection directly reduce perceived risk, while Klarna and Afterpay add trust through flexible payment transparency. You should use verified-purchase badges, clear seller ratings, and third-party seals (e.g., Norton, BBB) to reinforce credibility; at the same time, deploy behavioral signals such as recent purchase counters and post-purchase tracking updates, which convert abstract safety into immediate reassurance.
Reviews and Ratings in Online Shopping
Most shoppers consult peer feedback before committing: BrightLocal found that about 93% of consumers read online reviews for local businesses, and that tendency has carried into e-commerce where star ratings and review counts directly influence visibility and conversion. You’ll notice products with higher average ratings and substantial review volumes rank better in platform search results and often enjoy noticeably higher conversion rates, since many buyers use a four-star threshold as a quick filter for acceptable quality.
Platforms and brands are fighting review fraud with algorithmic detection, verified-purchase tags, and legal action; Amazon’s periodic purge of fake reviews and Trustpilot’s enhanced verification workflows are examples you can point to. Because fake or incentivized reviews are a persistent risk, undetected inauthentic reviews can instantly erode hard-earned trust, so you should prioritize moderation, encourage photo/video submissions, and highlight reviewer credibility to keep social proof reliable.
More detail: visual and contextual reviews now matter more than raw star averages-photos, short videos, and responses from sellers boost trust; Sephora’s user photo grid and Amazon’s video reviews both increase shopper confidence by showing real-world use. You should also monitor review velocity and sentiment trends: a sudden spike in negative reviews is an early indicator of product or fulfillment issues that, if addressed within 24-48 hours, prevents larger reputation problems.
The Role of Brand Reputation
Your brand’s reputation has broadened from product quality to include data privacy, sustainability, and public stances. Major reputation studies over the last five years show consumers factor ethics and transparency into buying decisions, and you’ll see measurable impacts: privacy lapses or supply-chain scandals depress purchase intent and social sentiment, while consistent, authentic ESG actions can increase loyalty and willingness to pay a premium. Crisis examples-platform data breaches or high-profile recalls-illustrate how quickly trust erodes when mitigation is slow or opaque.
Proactive reputation management scales trust: transparent policies, rapid customer support, and public remediation plans restore confidence faster than generic statements. You should integrate social listening, NPS tracking, and rapid-response PR protocols; brands that respond publicly within hours and offer tangible remediation (refunds, replacements, data protections) recover trust significantly faster than those that wait. A single data breach or unresolved service failure can undo months of positive engagement, so response speed and accountability are imperative.
More detail: operational measures such as quarterly privacy audits, supplier transparency reports, and publishing remediation timetables turn abstract reputation claims into verifiable actions you can cite in marketing and support. Tracking metrics-Net Promoter Score, CSAT, review sentiment, and share-of-voice-lets you quantify reputation shifts and link them to conversion and churn, so you can prioritize investments that actually protect and grow customer trust.
The Impact of Data Privacy Regulations
Overview of GDPR and Similar Regulations
Regulatory frameworks since 2018 have forced you to treat personal data as a business asset that carries legal obligations. The EU's GDPR (effective May 25, 2018) created rights such as access, rectification, erasure, portability and restriction of processing, and it empowers regulators with fines up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover. Comparable laws followed: California's CCPA (effective Jan 1, 2020) and its amendment CPRA (expanded protections effective 2023) give you rights to know, delete and opt-out of the sale of personal data, while Brazil's LGPD and other national laws mirror many of those principles.
Enforcement examples make the rules tangible: France's CNIL fined Google €50 million in 2019 for transparency and consent failures, illustrating how regulators convert consumer complaints into penalties. At the same time, the regulatory wave accelerated industry shifts-cookie banners, data-mapping, DPIAs and privacy-by-design are now standard operational workstreams and not just legal checkboxes.
Consumer Expectations for Data Protection
You now expect granular control over your data and immediate, understandable options to exercise those rights. A 2020 Cisco consumer survey found that about 84% of respondents consider privacy important when interacting with companies, and that sentiment translates into purchase behavior: clear opt-outs, easy deletion and explicit consent mechanisms increase your willingness to transact.
High-profile breaches taught you that weak practices have real consequences-Marriott's 2018 breach affected roughly 500 million guests, and Equifax's 2017 breach led to settlements in the hundreds of millions of dollars, reinforcing that security failures erode trust and can drive customer loss. You expect prompt notification: GDPR requires data controllers to report a personal data breach to authorities without undue delay and, where feasible, within 72 hours, and late or opaque responses damage the relationship as much as the breach itself.
More detail: you favor companies that adopt concrete safeguards-encryption at rest and in transit, multi-factor authentication, independent audits (SOC 2/ISO 27001) and privacy-enhancing technologies like anonymization or differential privacy. Examples such as Apple's privacy labels and App Tracking Transparency (iOS 14.5+) show that when platforms give you control, adoption of privacy-preserving defaults becomes a selling point rather than a compliance cost.
Trust versus Transparency in Online Transactions
Transparency alone doesn't buy trust; you evaluate both the information you receive and the actions companies take. A dense privacy policy that lists data categories but offers no easy controls or no history of responsible incidents feels hollow-conversely, concise, contextual disclosures paired with visible security practices tend to increase conversions and opt-in rates.
Practical signals matter: timely breach responses, easy-to-find privacy settings, and third-party attestations (security seals, audit summaries) are the behaviors that make you feel safe handing over payment details or personal preferences. Industry reports after ATT and GDPR-related shifts show that merchants who prioritize first-party data collection and clear value exchange outperform peers on retention and lifetime value.
More detail: operationalize trust by giving you simple controls (one-click deletion or export), transparent benefit statements (“we use this data to reduce delivery time by X”), and rapid incident workflows that notify affected users immediately. Those steps reduce churn and convert privacy investment into a measurable business advantage.
The Shift Towards Sustainability in Online Purchases
Growing Consumer Awareness of Sustainable Practices
You increasingly factor environmental impact into purchase decisions: studies like Nielsen (2015) found 66% of global consumers willing to pay more for sustainable brands, and follow-up research (IBM/NRF, 2020) showed roughly 57% of shoppers changed habits to reduce environmental impact during that period. You also see behavior-driven signals - higher click-throughs on listings with eco-labels, surge in product searches that include terms such as "carbon footprint" or "recycled materials," and social media communities that amplify supplier sourcing and labor practices.
Returns in online apparel (often cited as up to 30% of orders) and excessive single-use packaging are tangible pain points you notice when evaluating sustainability claims, because they directly increase emissions and waste throughout the fulfillment chain. You therefore reward brands that publish concrete metrics - product-level carbon footprints, third-party certifications (B Corp, Fair Trade, GOTS) - rather than vague promises, and you increasingly expect those metrics to be visible at checkout or on product pages.
Brands Responding to Ecological Concerns
Major players and challengers are responding with concrete programs: Patagonia's Worn Wear repair network, Allbirds' product-level carbon disclosures, IKEA's commitment to become a circular business by 2030, and Amazon's Climate Pledge Friendly label to surface lower-impact products. You now find retailers offering repair services, refillable options, and digital transparency tools such as QR-enabled supply-chain traceability to verify origin and material content.
At scale, consumer goods giants have tied sustainability to growth: Unilever reported that its Sustainable Living Brands grew significantly faster than the rest of the portfolio and were responsible for a large share of the company's recent overall growth, which pushed competitors to integrate eco-metrics into product development and marketing. You benefit when companies back claims with lifecycle assessments (LCA), third-party audits, and standardized labels that simplify comparison shopping.
Smaller brands leverage sustainability as a differentiator too: startups like Allbirds and Veja built customer acquisition around transparent carbon footprints and ethical sourcing, proving that measured transparency can drive loyalty and premium pricing. Meanwhile, the danger of greenwashing has prompted regulators and platforms to tighten rules, so you should expect fewer unverified claims and more verified labels over time.
The Future of Eco-Conscious Consumerism
Regulation and tech will reshape what you expect from online merchants: the EU's product sustainability and reporting frameworks (including Digital Product Passports and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) push manufacturers and retailers to publish standardized product data, and similar requirements are spreading worldwide. You’ll see more mandatory disclosures, clearer lifecycle data at point-of-sale, and integration of environmental scores into recommendation algorithms.
Operational changes will matter too - last-mile delivery optimization, consolidated shipments, and carbon-aware routing powered by AI can reduce emissions without asking you to change buying frequency. Packaging EPR schemes and reusable-return programs will also scale, making low-waste fulfillment a competitive necessity. At the same time, greenwashing remains a high-risk issue that could erode trust unless brands adopt verifiable metrics and third-party validation.
Expect technological enablers such as blockchain-based provenance records, automated LCA tools embedded in product creation, and standardized carbon labels to become common; these provide the data you need to compare products objectively and push the market toward genuinely lower-impact options.
Cross-Border E-Commerce
The Globalization of Online Shopping
Consumers increasingly treat borders as a convenience layer rather than a barrier: you discover niche brands on marketplaces like Amazon Global, AliExpress and Shein, and many merchants now list pricing in multiple currencies. Policy changes have shifted the economics - for example, the EU’s IOSS regime (effective July 1, 2021) changed VAT collection for goods under €150, and the United States still operates with a $800 de minimis threshold for most imported goods, both of which directly affect your landed costs and checkout friction.
Platforms and retailers respond by optimizing checkout and fulfillment: cross-border marketplaces routinize currency conversion, local returns addresses, and localized payment rails to reduce drop-off. You’ve seen this in practice when a seller offers local-language pages, displays taxes at checkout, and partners with regional carriers - those adjustments can increase conversion rates by a noticeable margin and make international SKUs behave like domestic ones.
Cultural Considerations in Consumer Behavior
Localization goes well beyond translation: you expect product descriptions, sizing, and imagery that reflect local norms - for instance, color associations differ (white is a celebratory color in some East Asian markets but a mourning color in others), and clothing sizes often require region-specific fits. Around three quarters of consumers prefer shopping in their native language, so you lose trust quickly if measurements, return policies, or customer service don’t match local expectations.
Payment preferences are another cultural fault line: in China you use Alipay or WeChat Pay; in parts of Europe you often see Klarna or SEPA transfers; in Latin America, boleto and installment payments remain common. Adapting to those preferences not only reduces abandonment but also affects average order value - offering installment options, for example, can lift order sizes in markets where they’re expected.
Trust signals differ too: in some markets third‑party seals and local influencers drive acceptance more than global brand badges, and you should tailor reviews, certification marks, and post‑purchase communications accordingly to lower perceived risk and improve repeat purchase rates.
Shipping and Logistics Challenges
Cross-border logistics create visible pain points for you: unpredictable delivery windows, customs delays, and duty surprises all increase cancellations and returns. Carriers routinely add 3-10 days for customs clearance, and duties/taxes can add 10-30%+ to the final price depending on category and country, which frequently becomes a surprise at delivery if not disclosed up front.
Returns amplify the problem - fashion and apparel returns often exceed 30% and international returns are expensive and operationally complex, forcing many merchants to localize reverse logistics or offer local refunds rather than shipping items back. You’ll notice competitive sellers mitigate this by establishing regional warehouses, using consolidated cross‑border hubs, or offering prepaid return labels through local partners.
Optimizing for cross-border success means mapping tax regimes, partnering with customs brokers, and presenting delivered‑price transparency at checkout; those investments reduce friction and the worst outcomes - lost orders, high return rates, and negative reviews - while enabling you to scale into new markets with predictable margins.
The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Consumer Behavior

AI-Powered Recommendations and Personalization
Personalization engines now determine what you see first, and that influences what you buy: Amazon’s recommendation system is estimated to account for roughly a third of its revenue, while streaming platforms report that recommendations drive a large majority of engagement (commonly cited at around 70-80% for top services). You encounter collaborative filtering, content-based, and hybrid models across touchpoints-email, on-site banners, push notifications and in-app feeds-so personalization is no longer just product suggestions but the primary interface shaping discovery and purchase paths.
Because models use real-time signals like session behavior, location, inventory and price sensitivity, you get offers tailored to the moment; companies that deploy these systems report measurable lifts-industry studies show personalization can boost revenue and conversion rates in the low double digits. At the same time over-personalization can create a narrow "filter bubble" that limits discovery, and evolving privacy rules plus cookie deprecation force teams to combine first-party data with device and contextual signals to maintain effective recommendations without violating consent.
Chatbots and Consumer Support
Chatbots now handle a significant share of routine support interactions, so you often get instant answers to balance inquiries, order status or simple returns without waiting for an agent; many organizations report bots resolving 20-40% of basic queries, cutting response times and improving availability. Examples include Bank of America’s Erica for financial nudges, Sephora’s virtual assistant for product guidance, and retail bots that book appointments or process refunds-these reduce workload on human agents and scale 24/7 support.
Advances in conversational AI and large language models let chatbots perform more complex tasks-contextual handoffs, personalized upsells and multi-turn troubleshooting-yet they also introduce risks: hallucinations, incorrect advice, and possible exposure of sensitive data when logs are mishandled. You should expect robust escalation paths and monitoring; firms that combine scripted flows with AI-based understanding and human-in-the-loop review tend to preserve satisfaction while keeping operational risk and compliance exposure lower.
Best practice for chatbots you deploy includes ongoing intent accuracy testing, clear fallback messaging, and transparent data-use notices: track containment/deflection rates, average handle time and escalation triggers, retrain models on resolved transcripts, and limit personally identifiable information in conversational logs to reduce liability and improve trust.
Predictive Analytics in Market Trends
Predictive models now underpin inventory planning, dynamic pricing and promotional timing, so you see prices and stock that react to demand signals in near real time-Amazon updates prices frequently, airlines update fares by the minute, and major retailers use ML to reduce stockouts and markdowns. Organizations that integrate demand-sensing with point-of-sale and supply-chain telemetry report inventory cost reductions and fewer lost-sales episodes, with many achieving mid- to high-single-digit improvements in working capital efficiency.
However, models are only as good as the data and assumptions behind them: sudden shocks like pandemics exposed how quickly forecasting accuracy can collapse when behavioral baselines shift, and unexamined training data can embed biases that misallocate inventory or misprice offers. To guard against that, you should combine causal analysis, scenario simulation and explainable models so forecasting informs strategy without becoming an opaque source of brittle decision-making.
Operationally, keep features fresh, monitor model drift, A/B test pricing and promotional strategies, and use human review for strategic decisions; pairing short-horizon demand sensing with longer-horizon causal forecasts helps you react to immediate changes while maintaining resilient plans.
The Rise of Subscription-Based Models
Understanding Subscription Economy
You can see how recurring-revenue businesses changed priorities: instead of one-off sales, firms chase monthly ARPU and lifetime value. Big-name pivots prove the point - Adobe's move to Creative Cloud in the early 2010s transformed its revenue base into predictable streams, Netflix grew its streaming business to >200 million subscribers by 2023, and Dollar Shave Club’s 2016 exit to Unilever for $1 billion showed how subscription-first brands create scalable, saleable value.
Operationally, you’ll notice companies track metrics like LTV:CAC ratios (a common healthy benchmark is around 3:1 for SaaS), churn, and MRR growth instead of single-sale KPIs. That shift forces continuous product improvements and data-driven personalization; in practice, it means your behavior - engagement, repeat frequency, and payment signals - becomes the product teams’ primary feedback loop.
Consumer Preferences for Convenience
You increasingly choose subscriptions because they remove friction: saved payment details, automated delivery, and curated discovery replace repeated decision-making. Services such as Amazon Subscribe & Save, HelloFresh, and Spotify turn habitual needs into a low-effort background task so you trade choice friction for time savings and consistency.
At the same time, convenience drives design choices that affect you directly - one-click renewals, smart reordering, and predictive recommendations. Those features increase retention: autoplay, algorithmic playlists, and suggested replenishments are subtle nudges that raise average usage and reduce the chance you cancel.
Beyond convenience, you also value control: flexible pause/cancel policies, easy plan upgrades, and transparent billing reduce perceived risk and make you more likely to try new subscriptions; when companies get that balance right, trial-to-paid conversion and long-term retention jump.
Long-term Relationships and Customer Loyalty
You benefit when companies focus on retention because sustainable margins come from keeping you engaged over years, not weeks. Subscription businesses invest in customer success, personalized communications, and tiered rewards to boost LTV; for example, loyalty-style benefits bundled into Amazon Prime create a retention moat that makes churn more costly for you and harder for competitors to overcome.
From a commercial perspective, you should know teams optimize for small improvements in churn and engagement: a 1% reduction in monthly churn materially increases lifetime value, and many subscription firms aim for usage-based upsells rather than constant acquisition. Metrics-driven loyalty programs, community features, and usage analytics combine to make the relationship feel ongoing rather than transactional.
Practically, that means you’ll see more brands offering tailored retention incentives - personalized discounts, content exclusives, and usage-based tiering - all designed to keep you inside an ecosystem where predictable revenue for the company aligns with convenience and value for you, while the persistent risk remains subscription fatigue and involuntary churn from payment failures.
Payment Evolution in Online Shopping
Traditional Payment Methods vs. Digital Payments
When you weigh traditional card rails against newer digital channels, cards still power the bulk of transactions in many markets, with stored-card convenience and one-click checkouts driving higher conversion for repeat customers. Legacy networks have optimized authorization speeds and merchant protections, yet you see clear gains from adding digital alternatives: Buy‑Now‑Pay‑Later (BNPL) typically lifts average order value by ~20-30% in fashion and electronics verticals, and tokenized cards reduce PCI scope and chargeback exposure.
Across regions, mobile wallets and local bank-transfer systems have reshaped user expectations-Alipay and WeChat Pay dominate China, while Apple Pay/Google Pay and local e‑wallets capture growing shares in Europe and North America. If you enable a mix of global cards, local wallets and alternative methods, conversion can improve substantially; merchants who support localized payment options frequently report conversion uplifts of up to 40% for cross‑border shoppers.
Cryptocurrency Adoption in E-Commerce
You've observed pilots from merchants like Overstock and integrations from processors such as BitPay, Coinbase Commerce and PayPal, but mainstream acceptance remains limited by volatility and regulatory complexity. The main upside for you as a merchant is lower cross‑border settlement friction and potential fee savings, especially when you accept stablecoins (USDC, USDT) to mitigate price swings; the main downside is legal/tax ambiguity and the reputational and compliance risks tied to illicit‑use concerns.
Adoption currently sits in the low single‑digit percentages of total e‑commerce volume, concentrated in tech, collectibles/NFT ecosystems and privacy‑focused storefronts. You’ll find that layer‑2 solutions and alternative chains (for example, Lightning Network for BTC, and rollups like Polygon or Optimism for Ethereum) cut gas fees and latency, making on‑chain checkout more viable for smaller purchases; still, most merchants hedge by converting crypto receipts to fiat immediately.
More practically, payment processors now offer automatic fiat settlement and custodial services so you don’t hold crypto exposure on your balance sheet-BitPay, for instance, gives instant conversion options to USD/EUR and settlement to your bank, lowering merchant risk. For compliance, you should plan for enhanced KYC/AML reporting and integrate tax tools that handle token gains/losses because instant‑conversion and compliant custody are the fastest routes to merchant adoption.
Security and Fraud Prevention Strategies
You confront escalating fraud vectors as payment options multiply: account takeover, friendly fraud/chargebacks and card‑testing remain top threats, and data breaches carry long‑term brand damage. Implementing tokenization, end‑to‑end encryption and adhering to PCI DSS reduces your attack surface, while device fingerprinting and behavioral analytics help spot anomalous sessions before payment authorization.
Risk‑based authentication is the pragmatic middle ground: apply friction selectively based on transaction risk score, use EMV 3‑D Secure v2 for stronger authentication in high‑risk cases, and deploy ML models that learn from your chargeback history to reduce false positives. Tools such as Stripe Radar, Adyen RevenueProtect and third‑party identity graphs can be integrated to automate decisions and keep conversion losses minimal; importantly, you should A/B test flows to quantify the tradeoff between security and checkout abandonment.
For deeper resilience, combine regulatory compliance with modern fraud controls-PSD2‑style Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) in Europe, tokenization for recurring billing, and continuous authentication via behavioral biometrics. Investing in ensemble ML systems plus a dedicated disputes team will shrink fraud losses and improve recovery rates, because the most effective strategy pairs automated prevention with human review and clear chargeback policies.
The Future of Online Consumer Behavior
Emerging Technologies and Trends
Generative AI is already changing how you discover and evaluate products: tools that produce personalized descriptions, dynamic imagery and conversational assistants cut content production time and can increase conversion when deployed well. McKinsey estimates AI’s potential economic impact in the private sector at roughly $2.6-$4.4 trillion annually, and you’ll see that reflected in commerce through automated merchandising, smarter recommendation engines and AI-driven customer service that handles a growing share of routine queries.
Augmented reality and live commerce continue to reshape purchase intent - major retailers like IKEA and Sephora use AR try-ons to reduce returns and boost basket size, and live-stream shopping that dominated in China (sales in the hundreds of billions of dollars annually in recent years) is scaling in Western markets via platforms such as TikTok and Amazon Live. At the same time, overreliance on third‑party identifiers and centralized tracking is risky: privacy rules and platform changes force you to prioritize first‑ and zero‑party data, edge computing and contextual relevance over brittle tracking models.
Anticipating Shifts in Consumer Expectations
Faster fulfillment windows and frictionless returns are rapidly becoming baseline expectations: shoppers once delighted by next‑day delivery now often expect options like same‑day or two‑hour delivery in urban markets, and retailers that can’t offer reliable, transparent logistics suffer lost conversions. You’ll need to map customer tolerance for wait times by segment and invest in micro‑fulfillment, local inventory visibility and partnerships with quick‑commerce players to stay competitive.
Beyond speed, you must deliver personalization that feels private and earned; customers increasingly demand transparent provenance, sustainability metrics and real-time inventory accuracy. Brands such as Patagonia and Everlane have shown that publishing supply‑chain details and environmental metrics can convert higher‑intent buyers, and integrating carbon labels or repair/buy‑back options will shift purchase decisions for a meaningful minority of consumers.
Operationally, expect returns and circularity to push new cost centers into your P&L: reverse logistics, refurbishment and resale platforms will be necessary investments if you want to capture value from post‑purchase lifecycles and meet the expectations set by sustainability‑forward competitors.
Preparing for the Next Generation of Online Shoppers
Gen Z and incoming Gen Alpha are shaping format and channel preferences: short‑form video, creator commerce and native social checkout dominate discovery for younger cohorts, and you’ll find engagement and conversion highest when commerce is embedded in those experiences. Brands that collaborate with micro‑influencers, prioritize authentic UGC and optimize for vertical video formats see outsized reach and lower CAC in this demographic.
Technically, you should prioritize mobile‑first UX, instant checkout flows (digital wallets, one‑tap payments) and progressive web apps that reduce load time; studies consistently show that every 100ms of delay can meaningfully reduce conversion, so speed and perceived responsiveness remain direct revenue levers. Also, gamification and loyalty tied to social identity will increase lifetime value among younger shoppers.
Practically, that means building creator programs, investing in modular tech stacks for rapid experiment cycles, and embedding social commerce pilots into your roadmap so you can iterate on content commerce formats without overhauling core systems; doing so positions you to capture lifetime value as these cohorts increase their share of spending.
Summing up
Conclusively, as you navigate the digital marketplace you find convenience, speed and personalization shaping expectations: mobile-first interfaces, frictionless checkout, tailored recommendations and subscription options make shopping faster and more habit-driven, while social proof and data-driven targeting push relevant offers to you across devices and channels.
Yet some fundamentals remain constant: you still prioritize trust, clear value and emotional resonance, and you continue to weigh risk and price for higher-consideration purchases; successful brands will therefore pair sophisticated technology with privacy-aware transparency and reliable service so you can transact with confidence across touchpoints.
FAQ
Q: How has the device mix and browsing context changed for online shoppers?
A: Mobile has moved from a secondary channel to the dominant browsing and purchasing context for many categories, with apps and progressive web apps driving faster, session-based interactions. Consumers now expect pages to load in under two seconds, optimized touch interactions, and contextual experiences (location, time of day). What hasn’t changed is the pattern of multi-session decision-making: shoppers still research across devices and come back before converting, so cross-device continuity and persistent carts remain important.
Q: What has changed about personalization and recommendations, and what remains the same?
A: Personalization has become far more data-driven and automated: real-time recommendations, dynamic content, and AI-curated feeds tailor product discovery to inferred intent and past behavior. At the same time, consumers are more sensitive to privacy and expect transparency about how data is used, so personalization must balance relevance with clear consent. What hasn’t changed is the basic consumer desire for relevance-people still respond best to useful, timely suggestions that simplify decision-making rather than intrusive or irrelevant targeting.
Q: How has social media and influencer activity affected purchasing behavior?
A: Social channels evolved from inspiration tools to direct commerce platforms: shoppable posts, live commerce, and short-form video heavily influence discovery and impulse purchases, especially among younger cohorts. User-generated content and peer validation now accelerate trust-building. What hasn’t changed is that authenticity and social proof drive conversions-consumers still rely on reviews, endorsements from people they trust, and clear product information before completing higher-value purchases.
Q: In what ways have payments, checkout flows, and fulfillment expectations shifted?
A: Checkout friction has been reduced by widespread adoption of digital wallets, one-click purchases, and flexible payment options like buy-now-pay-later, increasing conversion rates for mobile and impulse buys. Delivery expectations have tightened: faster shipping windows, tighter tracking, and easier returns are increasingly standard. What hasn’t changed is the importance of predictable, transparent policies-consumers continue to favor sellers who make costs, delivery timelines, and return processes simple and reliable.
Q: Which fundamental aspects of consumer behavior remain unchanged despite rapid digital shifts?
A: Core drivers-seeking value, minimizing risk, and preferring convenience-remain constants. Cognitive shortcuts such as price anchoring, social proof, and scarcity cues still shape choices. Trust and clarity continue to be decisive: accurate information, credible reviews, and straightforward customer service still convert wary shoppers into buyers. Businesses succeed by delivering consistent experiences, clear policies, and honest communications while adapting tactics (technology, channels, personalization) to contemporary consumer expectations.